News & Trends - MedTech & Diagnostics
A move towards smaller and more cost effective robotics
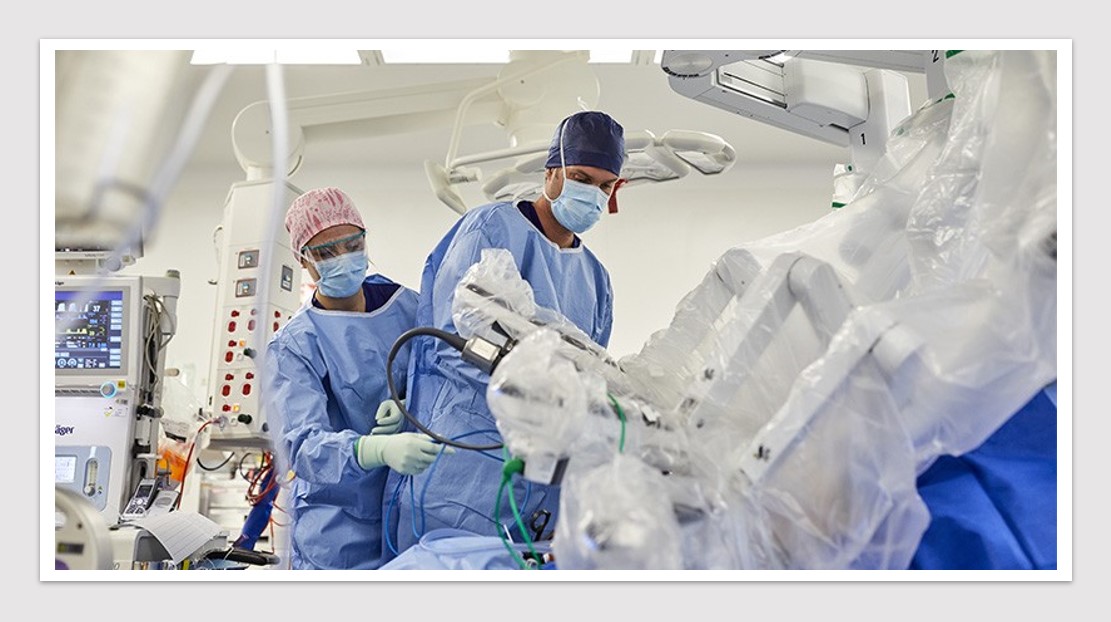
MedTech News: The 2022 American Urological Association (AUA) Annual Meeting included the International Prostate Forum with a discussion on the future of robotic technology for the treatment of prostate cancer, highlighting the movement towards newer, smaller and more cost effective robotic approaches.
According to Dr Isaac Kim, Professor of Urology, Yale School of Medicine, the Intuitive Surgical’s Da Vinci Xi has beenn the dominant surgical platform in prostate cancer. However, there are significant shortcomings including its cost, size and lack of haptic feedback.
The first true alternative to the Da Vinci system was the REVO-I-robotic surgical system which was developed in South Korea and received the first regulatory approval in 2018. Fundamentally, it utilises similar technology to the Da Vinci platform including the surgeon control console, a four-arm robotic operation card, and a high-definition vision cart. However, it offers haptic feedback and costs approximately 42% less than the Da Vinci system.
The next surgical robotic platform Dr Kim discussed is the Hugo RAS from Medtronic. This is a modular system and as a result this platform is more economical. There is an open consult and improved surgeon interface. The first case using this platform was performed June 22, 2021 when a patient underwent radical prostatectomy in Chile. Since then, there has been approval in India (September 2021), Europe (October 2021), and Canada (December 2021). The FDA IDE in the United States was May 2021.
Additionally, Robot Surgical has developed the BITRACK platform. While the technology development of this platform has been completed, it is still awaiting clinical use. The robotic platform uses three arms with open remote control. As a result, there is a smaller footprint than the Da Vinci system and costs are expected to be substantially lower.
In terms of innovations to advance on the current approach, Dr Kim emphasised the value and importance of haptic feedback. Robotic surgical platforms intrinsically dissociate a surgeon’s hands from the tissue. True haptics requires two fundamental features: tissue perception and motion perception. For experienced surgeons, visual haptics may supplant tactile feedback.
The Senhance laparoscopic surgical robot was the first system with haptic feedback. This was developed and subsequently received FDA approval in 2017. However, this system is still cost prohibitive in many settings, costing approximately $1.5 million.
In parallel to work on haptics, there has been an effort to decrease the size of surgical robots. Perhaps the most clinically utilised of these is the Da Vinci SP (Single Port) system. The platform further has a smaller footprint and improved mobility while preserving the intuitive controls that surgeons who have used the Da Vinci XI system are used to. In comparison to the Xi system, Dr Kim noted that the SP system includes instruments with elbows and shoulders though these are relatively weaker, the camera is flexible, and energy options are relatively limited without an available stapler. These highlight some of the engineering limitations of the SP system that Dr Kim then emphasised. First, there is an instrument registration delay and limitations in instrument engineering. Further, the instrument shafts are not stiff, limiting the ability for a surgeon to perform blunt dissection. In terms of the camera, it fogs “too easily” and manipulation is not intuitively obvious. Finally, the sweet spot is 15 to 25cm away from the target and the working area is “limited to that of a tennis ball”.
Moving from laparoscopic approaches to endoscopic robots, Dr Kim then discussed the Monarch Robot from Johnson & Johnson which allows for remote controlled ureteroscopy and PCNL, with improved percutaneous access and the potential for dual ureteroscopic and percutaneous surgery. Further, the device has simultaneous lithotripsy and suction which may increase stone free rates. However, there are still significant barriers to its use including cost (exceeding $1 million USD for the base), difficulty with guided access via ureteroscopy for staghorn stones, and a limitation in stone size via ureteroscopic lithotripsy.
He noted that there are numerous robots with more meaningful reductions in size that are beginning to come on the market. These include Versius from Cambridge Medical Robotics which uses individual cards and an open operator console with control via a joystick. Other platforms including the Surgibot-Spider from Transenterix (which has significantly lower cost and single port capability) as well as MicroSurge from DLR Institute of Robotics and Mechatronics). However, Dr Kim suggested that further miniaturization is inevitable with examples including single port orifice robotic technology, a miniature in vivo robot, and numerous others.
However, he cautioned the need for appropriate training on these novel approaches. The current training paradigm relies on some modification of the historical “see one, do one, teach one” principle. However, unlike open surgery, only one surgeon is actively in control at a time. Thus, he highlighted that there are no “do-overs”. In the context of robotic surgical innovation, the learning curve for the SP approach in terms of safety has been longer and slower and steeper than initially anticipated.
While advances in surgical robotic technology offer huge potential for innovation and patient care, patient safety and surgical outcomes need to be preserved during the learning curve.
News & Trends - MedTech & Diagnostics
Bariatric surgery trumps Novo Nordisk’s Wegovy in cost-effectiveness and durability
MedTech & Diagnostics News: Bariatric surgery emerges as cost-effective, boasting superior and enduring weight loss outcomes over a five-year span […]
MoreNews & Trends - Pharmaceuticals

Aussie digital health company hits new milestone in AstraZeneca partnership
Pharma News: Fewer than 50% of asthma patients adhere to their prescribed preventative medications. An Australian digital health company has […]
MoreDigital & Innovation
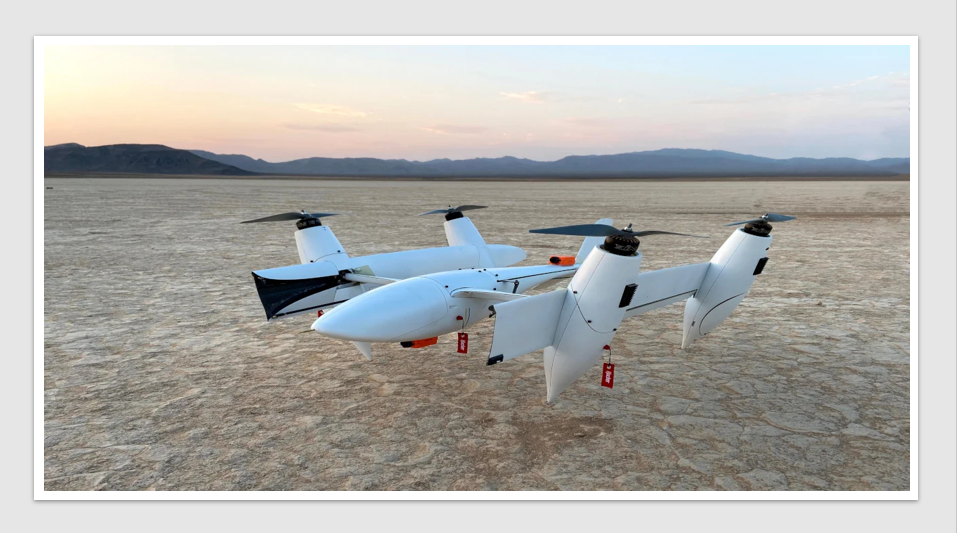

Medical drone to reduce health equity gaps in rural and remote Australia
A specialised medical drone which increases accessibility to essential health services such as pathology, medicines, and telehealth services in rural […]
More