News & Trends - MedTech & Diagnostics
Breakthrough blood test detects positive COVID-19 results in 20 minutes
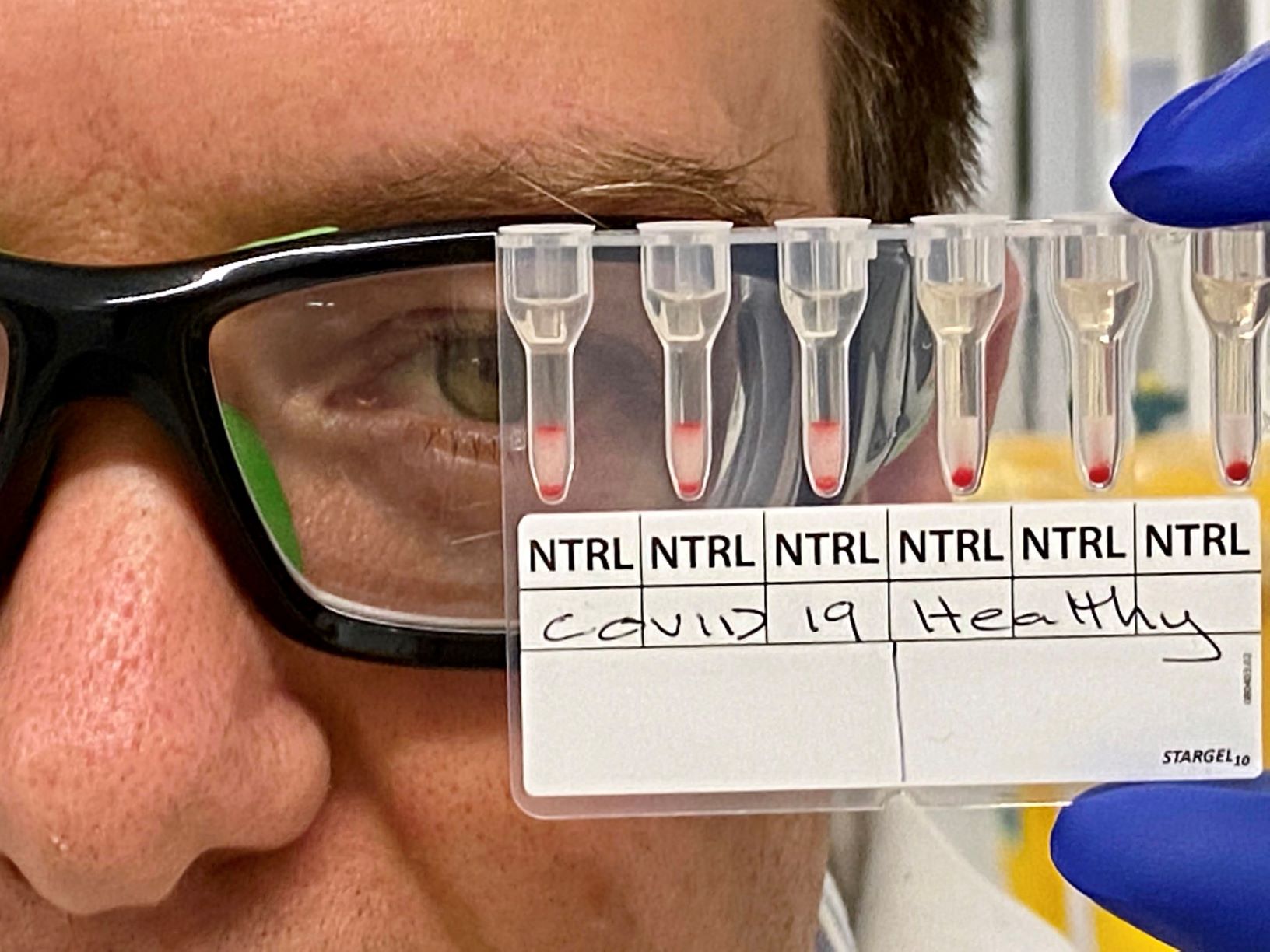
MedTech News: World-first research by Monash University has been able to detect positive COVID-19 cases using a simple, rapid, and easily scalable approach.
In a discovery that could advance the worldwide effort to limit the community spread of COVID-19 through robust contact tracing, researchers were able to identify recent COVID-19 cases using 25 microlitres of plasma from blood samples.
The research team developed a simple agglutination assay – an analysis to determine the presence and amount of a substance in blood – to detect the presence of antibodies raised in response to the SARS-CoV-2 infection.
Researchers were able to retrieve positive or negative readings in about 20 minutes.
While the current swab / PCR tests are used to identify people who are currently positive with COVID-19, the agglutination assay can determine whether someone had been recently infected once the infection is resolved – and could potentially be used to detect antibodies raised in response to vaccination to aid clinical trials.
Using a simple lab setup, this discovery could see medical practitioners across the world testing up to 200 blood samples an hour. At some hospitals with high-grade diagnostic machines, more than 700 blood samples could be tested hourly – about 16,800 each day.
Study findings could help high-risk countries with population screening, case identification, contact tracing, confirming vaccine efficacy during clinical trials, and vaccine distribution.
A patent for the innovation has been filed and researchers are seeking commercial and government support to upscale production.
Dr Corrie, Senior Lecturer in Chemical Engineering at Monash University and Chief Investigator in the CBNS, said “The findings were exciting for governments and healthcare teams across the world in the race to stop the spread of COVID-19. He said this practice has the potential to become upscaled immediately for serological testing.
“Detection of antibodies in patient plasma or serum involves pipetting a mixture of reagent red blood cells (RRBCs) and antibody-containing serum/plasma onto a gel card containing separation media, incubating the card for 5-15 minutes, and using a centrifuge to separate agglutinated cells from free cells,” Dr Corrie said.
“This simple assay, based on commonly used blood typing infrastructure and already manufactured at scale, can be rolled out rapidly across Australia and beyond. This test can be used in any lab that has blood typing infrastructure, which is extremely common across the world.”
“We found that by producing bioconjugates of anti-D-IgG and peptides from SARS-CoV-2 spike protein, and immobilising these to RRBCs, selective agglutination in gel cards was observed in the plasma collected from patients recently infected with SARS-CoV-2 in comparison to healthy plasma and negative controls,” Professor Gil Garnier, Director of BioPRIA, said.
“Importantly, negative control reactions involving either SARS-CoV-2-negative samples, or RRBCs and SARS-CoV-2-positive samples without bioconjugates, all revealed no agglutination behaviour.”
Professor Banaszak Holl, Head of Chemical Engineering at Monash University, commended the work of talented PhD students in BioPRIA and Chemical Engineering who paused their projects to help deliver this game changing COVID-19 test.
“This simple, rapid, and easily scalable approach has immediate application in SARS-CoV-2 serological testing, and is a useful platform for assay development beyond the COVID-19 pandemic. We are indebted to the work of our PhD students in bringing this to life,” Professor Banaszak Holl said.
“Funding is required in order to perform full clinical evaluation across many samples and sites. With commercial support, we can begin to manufacture and roll out this assay to the communities that need it. This can take as little as six months depending on the support we receive.”
COVID-19 has caused a worldwide viral pandemic, contributing to nearly 600,000 deaths and more than 13.8 million cases reported internationally. Australia has reported 10,810 cases and 113 deaths (figures dated 17 July 2020).
News & Trends - MedTech & Diagnostics

Pathology reforms: Frozen fees, windfall gains, and the fight for bulk-billing
Diagnostics & MedTech News: For nearly a quarter-century, pathology fees have remained stagnant, a situation deemed patently unfair by Australian […]
MoreNews & Trends - Pharmaceuticals
Call for coordinated policy and cross jurisdiction funding in chronic disease
Pharma News: The life expectancy of Australians is still rising, however the increased prevalence of chronic conditions and co- and […]
MoreNews & Trends - MedTech & Diagnostics

Expansion of hospital services for patients in NSW Macarthur region
MedTech & Diagnostics News: Marking a historic milestone with NSW Deputy Premier Prue Car and Health Minister Ryan Park, Campbelltown […]
MoreNews & Trends - Biotechnology
Superiority of cell-based flu vaccine revealed in RWE study
Biotech News: Vaccines stand as the primary strategy to mitigate the considerable morbidity, mortality, and economic burden associated with influenza. […]
More